WHAT IS TRIGGER FINGER?
Trigger finger disease is the condition regarding the tendons enabling the movement of the fingers. Tendons are the edges of the muscles in the arms. In other words, they are the thread-like tissues making the muscles stick to the tissues and transmit the power. We can consider the tendons as the threads transmitting the power of the muscles to the bones as to provide the movements of the fingers. After the tendon called threads are transmitted to the fingers, they are covered by circinate tissues called pulley preventing the movement of the tendons to the right or left (figure 1). The tendons move within this circles as the train passing through a tunnel. Under some conditions, the pulley tissue gets extremely thickhened and pressurises the tendon. As a result, there occurs some nodules on the tendon tissue. When we try to move our finger, this nodule forces the pulley but cannot pass through due to the constriction (figure 2). Thus, the finger cannot open and gets stuck (figure 3). If it is forced a little bit more with worry, the nodule suddenyl gets through the pulley and the finger opened. This mechanism is called trigger finger. The nodule passing through the pulley with force causes reaction and edema . this results in the increase of the triggering and it gets into a vicious circle. This condition can also be called as inflammation. In some cases, the finger can get completely locked.
There are two forms of trigger finger disease:
1-Trigger finger observed with the kids starting as of the neonatal period (figure 4). It is also called as congenital. It is commonly observed in the thumb. Congenital means the pathology observed in the early period after the delivery and does not indicate a genetical or chromosomal abnormality. In other wordsi pathology is not transmitted genetically and the cause is not known.
2-Trigger finger observed with the adults (figure 5). Again, the occurence mechanism or the cause of the disease is not clearly knwon. Local trauma can be the initiator factor. Although trigger finger is more frequently seen with the patients having diabetes, gout or rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatism ), there is no cause and effect relation between them. Every diabetics patient should not be expected to have trigger finger while every trigger finger patient should not be expected to have diabetics, etiher.
HOW TO DIAGNOSE?
The most important symptoms are the pain, force and pressure with finger movements and sticking and triggering in the next stages. Sticking and triggering occur with the finger movements. It does not occur while resting.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
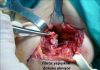
The purpose of the treatment is to relieve the pain, sticking and triggering and to provide normal hand functions. The tools called splints keeping the finger stabile can be used with anti-inflammatory medications. Though the the pain is relieved in the early period, the triggering recurs in most of the patients. Most of the relevant studies shows that the corticosteroid (cortisone) injection (needle) duly performed to the painful area has relieving effect. It is observed that supporting the injection with the splint does not change the result. This injection can safely be made suring pregnancy and breast-feeding period. For the patient with unsuccessful results, surgery is the only option. During bthe surgery, the surrounding artery/nerve packages are carefully preserved, the thickened pulley covering the tendons is cut and the tendons are released (figure 6, 7).
WHAT IS THE PROGRESS OF THE SURGERY, WHAT IS AHEAD OF US?
Orthopedician or Hand Surgeon examination is very important. The surgery is mostly performed with daycase hospitalization. There is no need for general anesthesia. Applying local (axillary block or RIVA) is generally sufficient. It is very important for you to mention about your special conditions (chronic diseases, regularly taken medication) during your consultation with the hand surgeon. Cold application and keeping the hand above the heart level in the postop early period (the first 3 days) will relieve the pain and throbbing. The bandage is generally opened within 5th-7th days and the wound is controlled. If there is no complication, you can take shower. Physical therapy and rehabilitation is rarely nweed at the end of this period. Even though the process changes in accordance with the surgery periormed and the condition of your wrist, it is expected to get back to normal life within 2-3 weeks.
PROBABLE COMPLICATIONS
The most important complication is the injury or cut of the artery/nerve (digital nerve/artery) around the surgical area. The surgery should be performed under microscope. In case of the injury of the nerve, a troubled and long period starts.
Another probable complication is the insufficient opening of the pulley. In this casei the surgery should be performed again. The other probable complications are limitation of finger movements due to the tissue adhesion on the surgical wound area, chronic pain (RSD), getting late or never getting the expected results.